Over the Counter (OTC) Hearing Aids Frequently Asked Questions
Over the counter (OTC) hearing aids are now available for sale online and in many stores. You may have questions about if OTC hearing aids will work for you. Use these FAQ to help you understand the import steps in determining the best type of hearing aid for you.
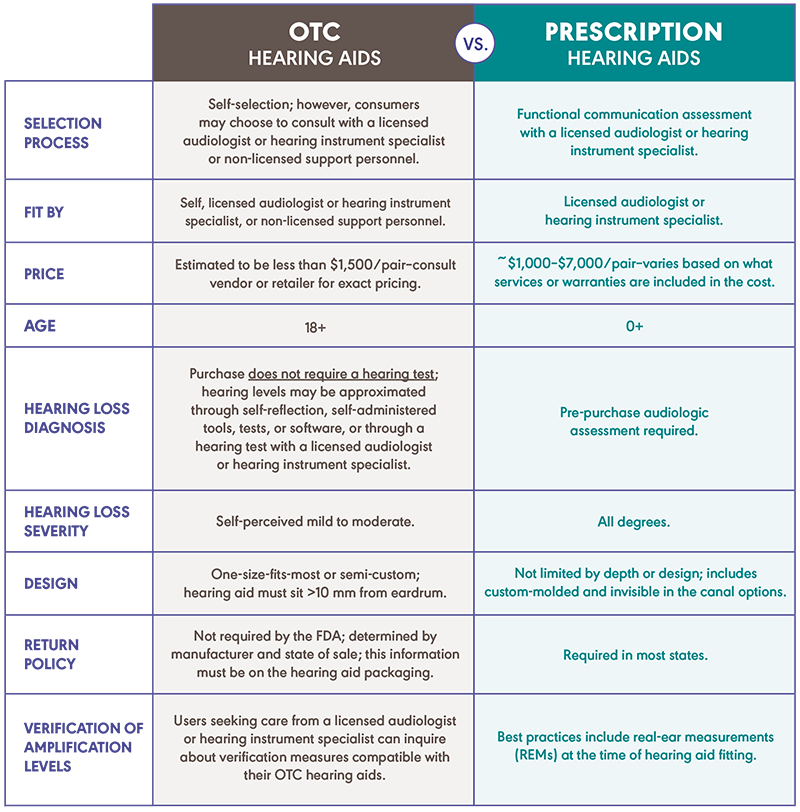
How much will OTC hearing aids cost?
It is estimated that OTC hearing aids will cost less than $1,500 per pair. It is best to consult with a vendor or retailer for exact pricing.
How will I know if OTC hearing aids will work for me?
The best way to know if OTC hearing aids will work for you is to see an audiologist for a comprehensive hearing evaluation. This evaluation will show you the degree of hearing loss and the part of the ear—outer, middle, or inner—that is causing your hearing loss. This information, taken together, will help you decide whether an OTC hearing aid is your best choice or if your needs would be better addressed by a prescription hearing aid.
Important Note: OTC hearing aids are purchased based on your own judgment. OTC aids will only work for you if your loss is mild to moderate. It is easy to over or underestimate your hearing difficulty. The most accurate diagnosis is made by an audiologist.
Who can wear OTC hearing aids?
OTC hearing aids may work well for you if you have a mild to moderate hearing loss. They are not effective for a moderate to severe degree of hearing loss. You must be 18 years or older to wear OTC hearing aids. Children should never wear them. You must consult a medical provider before buying an OTC hearing aid if you have any of the following medical conditions:
- ear deformity
- fluid, pus, or blood coming from the ear
- hearing loss or ringing (tinnitus) that occurs in only one ear or that is noticeably different in one ear
- pain or discomfort in the ear
- history of excessive earwax or feeling that something is in the ear
- sudden, quickly worsening, or fluctuating hearing loss
- vertigo or severe dizziness
Note: Individuals with cognitive or dexterity issues may not be suitable candidates for OTC hearing aids and should seek a consultation with an audiologist for hearing loss management.
Who can help me pick an OTC hearing aid?
Many places may sell OTC hearing aids: your local pharmacy, big-box stores such as Walmart, or online providers. You will make the decision about what you buy, just like any other item on the shelf. You may be able to ask store staff for help; however, these staff members likely do not have specialized training in hearing loss and hearing technology programming. It is important to read all information on the box before buying a device. You may not be able to return the hearing aids once you buy them.
Audiologists are trained hearing health care professionals with either a doctoral or a master’s degree. They can explain your hearing loss and help you consider the hearing aid that is best for you. Some audiologists will help you with basic maintenance of your OTC hearing aid for a service fee.
Why should I see an audiologist even if I choose an OTC hearing aid?
An audiologist is the expert in hearing health care—they can help you find a device and supply tips for you and your individual hearing needs. They will also be able to check your hearing over time to see if it remains stable or worsens. Regular check-ins are important; they reveal whether your chosen hearing aid (OTC or prescription) is providing enough sound to meet your hearing needs—or whether you and your audiologist should discuss other options. The common goal between you as the patient and the audiologist as the provider is to help you create a plan and a path toward improved hearing.
How do I find an audiologist in my area?
The American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) has a national directory that can help you find an audiologist in your area. Visit www.asha.org/profind/ or email ASHA Audiology Practices at audiology@asha.org.